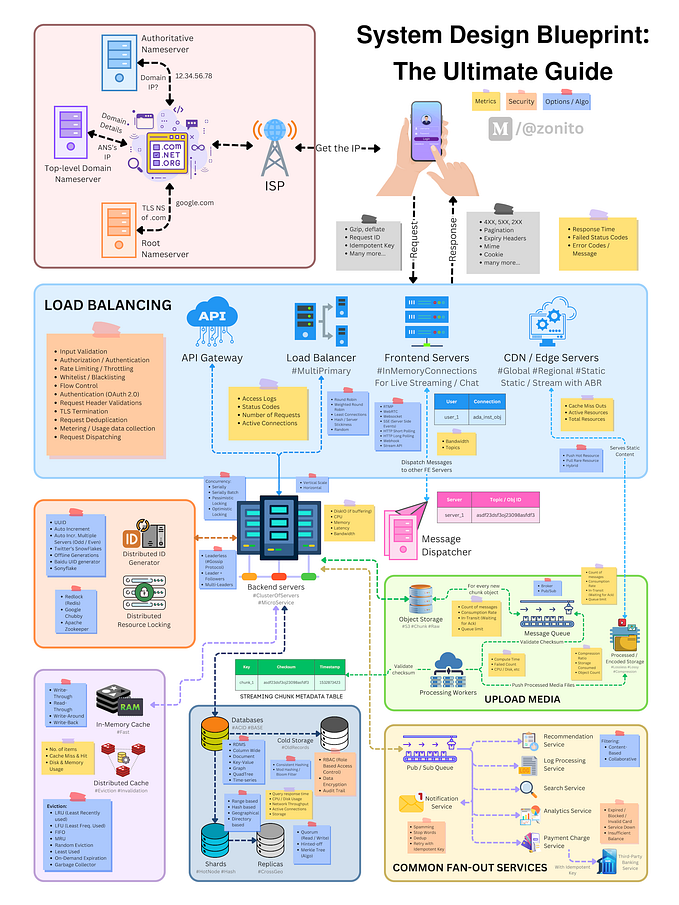
The Memento design pattern is a behavioral design pattern that allows an object to save and restore its state without violating encapsulation. The pattern is used when we want to be able to undo or rollback operations, or when we want to save the history of an object’s changes.
In this article, we’ll go over the details of the Memento pattern and provide a Java code example to demonstrate how it works.
Key Concepts of the Memento Design Pattern
The Memento pattern involves three key concepts: the Originator, the Memento, and the Caretaker.
Originator
The Originator is the object that has an internal state that needs to be saved and restored. In other words, it is the object that we want to be able to undo or rollback its changes.
Memento
The Memento is an object that stores the internal state of the Originator. It is the snapshot of the Originator’s state that we want to save.
Caretaker
The Caretaker is an object that manages the Mementos. It is responsible for storing the Mementos and providing them to the Originator when needed to restore its state.
When to Use the Memento Design Pattern
The Memento pattern is useful in situations where we want to be able to undo or rollback operations, or when we want to save the history of an object’s changes. It can be used in many different scenarios, such as:
- Text editors that allow undo and redo operations
- Graphic design tools that allow undo and redo operations
- Games that allow the player to undo or rollback their moves
- E-commerce websites that allow the user to cancel an order or revert to a previous order status
Example of Memento Design Pattern in Java
Let’s look at a Java code example to see how the Memento pattern can be implemented.
Suppose we have a drawing application that allows the user to create, modify, and delete shapes on a canvas. We want to use the Memento pattern to allow the user to undo or redo their shape modifications.
Here is the Java code for our drawing application:
import java.awt.*;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
public class Canvas {
private List<Shape> shapes;
private List<CanvasMemento> mementos;
private int currentIndex;
public Canvas() {
this.shapes = new ArrayList<>();
this.mementos = new ArrayList<>();
this.currentIndex = -1;
}
public void addShape(Shape shape) {
shapes.add(shape);
save();
}
public void removeShape(Shape shape) {
shapes.remove(shape);
save();
}
public void modifyShape(Shape shape, Color color, Point position) {
shape.setColor(color);
shape.setPosition(position);
save();
}
public void undo() {
if (currentIndex > 0) {
currentIndex--;
CanvasMemento memento = mementos.get(currentIndex);
restoreMemento(memento);
}
}
public void redo() {
if (currentIndex < mementos.size() - 1) {
currentIndex++;
CanvasMemento memento = mementos.get(currentIndex);
restoreMemento(memento);
}
}
public List<Shape> getShapes() {
return shapes;
}
private void save() {
List<ShapeMemento> shapeMementos = new ArrayList<>();
for (Shape shape : shapes) {
shapeMementos.add(shape.save());
}
CanvasMemento memento = new CanvasMemento(shapeMementos);
if (currentIndex == mementos.size() - 1) {
mementos.add(memento);
} else {
mementos.set(currentIndex + 1, memento);
}
currentIndex++;
}
private void restoreMemento(CanvasMemento memento) {
List<ShapeMemento> shapeMementos = memento.getShapeMementos();
shapes.clear();
for (ShapeMemento shapeMemento : shapeMementos) {
Shape shape = shapeMemento.restore();
shapes.add(shape);
}
}
private class CanvasMemento {
private final List<ShapeMemento> shapeMementos;
private CanvasMemento(List<ShapeMemento> shapeMementos) {
this.shapeMementos = shapeMementos;
}
private List<ShapeMemento> getShapeMementos() {
return shapeMementos;
}
}
}abstract class Shape {
private Color color;
private Point position;
public Shape(Color color, Point position) {
this.color = color;
this.position = position;
}
public Color getColor() {
return color;
}
public void setColor(Color color) {
this.color = color;
}
public Point getPosition() {
return position;
}
public void setPosition(Point position) {
this.position = position;
}
public abstract ShapeMemento save();
public abstract void restore(ShapeMemento memento);
}class Rectangle extends Shape {
private int width;
private int height;
public Rectangle(Color color, Point position, int width, int height) {
super(color, position);
this.width = width;
this.height = height;
}
public int getWidth() {
return width;
}
public void setWidth(int width) {
this.width = width;
}
public int getHeight() {
return height;
}
public void setHeight(int height) {
this.height = height;
}
@Override
public ShapeMemento save() {
return new RectangleMemento(getColor(), getPosition(), getWidth(), getHeight());
}
@Override
public void restore(ShapeMemento memento) {
RectangleMemento rectangleMemento = (RectangleMemento) memento;
setColor(rectangleMemento.getColor());
setPosition(rectangleMemento.getPosition());
setWidth(rectangleMemento.getWidth());
setHeight(rectangleMemento.getHeight());
}
}class Circle extends Shape {
private int radius;
public Circle(Color color, Point position, int radius) {
super(color, position);
this.radius = radius;
}
public int getRadius() {
return radius;
}
public void setRadius(int radius) {
this.radius = radius;
}
@Override
public ShapeMemento save() {
return new CircleMemento(getColor(), getPosition(), getRadius());
}
@Override
public void restore(ShapeMemento memento) {
CircleMemento circleMemento = (CircleMemento) memento;
setColor(circleMemento.getColor());
setPosition(circleMemento.getPosition());
setRadius(circleMemento.getRadius());
}abstract class ShapeMemento {
private final Color color;
private final Point position;
public ShapeMemento(Color color, Point position) {
this.color = color;
this.position = position;
}
public Color getColor() {
return color;
}
public Point getPosition() {
return position;
}
public abstract Shape restore();
}
}class RectangleMemento extends ShapeMemento {
private final int width;
private final int height;
public RectangleMemento(Color color, Point position, int width, int height) {
super(color, position);
this.width = width;
this.height = height;
}
public int getWidth() {
return width;
}
public int getHeight() {
return height;
}
@Override
public Rectangle restore() {
return new Rectangle(getColor(), getPosition(), getWidth(), getHeight());
}
}class CircleMemento extends ShapeMemento {
private final int radius;
public CircleMemento(Color color, Point position, int radius) {
super(color, position);
this.radius = radius;
}
public int getRadius() {
return radius;
}
@Override
public Circle restore() {
return new Circle(getColor(), getPosition(), getRadius());
}
}In this example, we have a code Canvasclass that represents the drawing canvas. The class has a Shapes field that stores the shapes on the canvas, a mementos field that stores the mementos of the canvas, and a currentIndex field that represents the current position in the mementos list.
The Canvasclass has a constructor that initializes the shapes, mementos, and currentIndex fields.
The addShape method allows the user to add a shape to the canvas. The method takes a Shape parameter shape that represents the shape to add. The method adds the shape to the shapes list and then calls the save method to create a new memento for the canvas.
The removeShape method allows the user to remove a shape from the canvas. The method takes a Shape parameter Shape that represents the shape to remove. The method removes the shape from the shapes list and then calls the save method to create a new memento for the canvas.
The modifyShape method allows the user to modify a shape on the canvas. The method takes a Shape parameter shape that represents the shape to modify, a Color parameter color that represents the new color of the shape, and a Point parameter Position that represents the new position of the shape. The method sets the color and position fields of the shape and then calls the save method to create a new memento for the canvas.
The undo method allows the user to undo the last shape modification performed on the canvas. The method checks if the currentIndex is greater than 0, which means that there is a previous memento to restore. If there is, the method retrieves the previous memento from the memento list and restores the shapes on the canvas to their previous states. The currentIndex is then decremented to represent the current position in the mementos list.
The redo method allows the user to redo the last shape modification performed on the canvas. The method checks if the currentIndex is less than the size of the mementos list minus 1, which means that there is a next memento to restore. If there is, the method retrieves the next memento from the mementos list and restores the shapes on the canvas to their next states. The currentIndex is then incremented to represent the current position in the mementoslist.
The getShapes method returns the shapes on the canvas.
The save method creates a new CanvasMemento object with the current state of the shapes on the canvas and adds it to the mementos list. If the currentIndex is not at the end of the mementos list, which means that there are future mementos that need to be deleted, the method replaces the future mementos with the new memento.
The restoreMemento method restores the shapes on the canvas to the state stored in a CanvasMemento object.
The CanvasMemento class represents a memento for the canvas and stores the mementos of the shapes on the canvas. The class has a private constructor that takes a List<ShapeMemento> parameter shapeMementos and a private method getShapeMementos that returns the shapeMementos field.
The Shape abstract class represents a shape on the canvas. The class has a color field that stores the color of the shape, a position field that stores the position of the shape, and abstract methods save and restore that allow the shape to save and restore its state.
The Rectangle class extends the Shape class and represents a rectangle on the canvas. The class has width and height fields that store the dimensions of the rectangle, a constructor that initializes the fields, getter and setter methods for the fields, and implementations of the save and restore methods.
The Circle class extends the Shape class and represents a circle on the canvas. The class has a radius field that stores the radius of the circle, a constructor that initializes the field, getter and setter methods for the field, and implementations of the save and restore methods.
list and then calls thesave` method to create a new memento for the canvas.
The modifyShape method allows the user to modify a shape on the canvas. The method takes a Shape parameter shape that represents the shape to modify, a Color parameter color that represents the new color of the shape, and a Point parameter position that represents the new position of the shape. The method sets the color and position fields of the shape and then calls the save method to create a new memento for the canvas.
The undo method allows the user to undo the last shape modification performed on the canvas. The method checks if the currentIndex is greater than 0, which means that there is a previous memento to restore. If there is, the method retrieves the previous memento from the mementos list and restores the shapes on the canvas to their previous states. The currentIndex is then decremented to represent the current position in the mementos list.
The redo method allows the user to redo the last shape modification performed on the canvas. The method checks if the currentIndex is less than the size of the mementos list minus 1, which means that there is a next memento to restore. If there is, the method retrieves the next memento from the mementos list and restores the shapes on the canvas to their next states. The currentIndex is then incremented to represent the current position in the mementos list.
The getShapes method returns the shapes on the canvas.
The save method creates a new CanvasMemento object with the current state of the shapes on the canvas and adds it to the mementos list. If the currentIndex is not at the end of the mementos list, which means that there are future mementos that need to be deleted, the method replaces the future mementos with the new memento.
The restoreMemento method restores the shapes on the canvas to the state stored in a CanvasMemento object.
The CanvasMemento class represents a memento for the canvas and stores the mementos of the shapes on the canvas. The class has a private constructor that takes a List<ShapeMemento> parameter shapeMementos and a private method getShapeMementos that returns the shapeMementos field.
The Shape abstract class represents a shape on the canvas. The class has a color field that stores the color of the shape, a position field that stores the position of the shape, and abstract methods save and restore that allow the shape to save and restore its state.
The Rectangle class extends the Shape class and represents a rectangle on the canvas. The class has width and height fields that store the dimensions of the rectangle, a constructor that initializes the fields, getter and setter methods for the fields, and implementations of the save and restore methods.
The Circle class extends the Shape class and represents a circle on the canvas. The class has a radius field that stores the radius of the circle, a constructor that initializes the field, getter and setter methods for the field, and implementations of the save and restore methods.
The ShapeMemento abstract class represents a memento for a shape on the canvas. The class has color and position fields that store the color and position of the shape at the time the memento was created, and an abstract restore method that allows the shape to restore its state.
The RectangleMemento class extends the ShapeMemento class and represents a memento for a rectangle on the canvas. The class has width and height fields that store the dimensions of the rectangle at the time the memento was created, a constructor that initializes the fields, getter methods for the fields, and an implementation of the restore method.
The CircleMemento class extends the ShapeMemento class and represents a memento for a circle on the canvas. The class has a radius field that stores the radius of the circle at the time the memento was created, a constructor that initializes the field, getter methods for the field, and an implementation of the restore method.
Conclusion
In this article, we have demonstrated how the Memento design pattern can be used in a drawing application to allow the user to undo or redo their shape modifications. The pattern allows us to save and restore the state of objects without violating encapsulation. We hope this article has been helpful in understanding the Memento pattern and how it can be applied in your own software projects.